CockroachDB Cloud is a fully-managed deployment of CockroachDB. This page describes CockroachDB Cloud's architecture and how it relates to CockroachDB.
For an intro to CockroachDB's core architecture and capabilities, see CockroachDB Architecture or take the free Introduction to Distributed SQL and CockroachDB course on Cockroach University.
CockroachDB Cloud terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Serverless cluster | A CockroachDB cluster billed and scaled according to the resources consumed by the cluster. |
| Dedicated cluster | A CockroachDB cluster billed according to the resources provisioned for the cluster. |
| Request Unit (RU) | Represents the compute and I/O resources used by a query. All database operations in CockroachDB Serverless cost a certain amount of RUs depending on the resources used. For example, a "small read" might cost 2 RUs, and a "large read" such as a full table scan with indexes could cost a large number of RUs. You can see how many Request Units your cluster has used on the Cluster Overview page. |
| spend limit | The maximum amount of money you want to spend on a cluster in a particular billing period. The amount you are billed is based on the resources the cluster used during that billing period. A cluster's budget is allocated across storage and burst performance. |
| baseline performance | The minimum compute and I/O performance that you can expect from your cluster at all times. This is 100 RUs per second for all Serverless clusters (free and paid). The actual usage of a cluster may be lower than the baseline performance depending on application traffic, because not every application will need 100 RUs per second at all times. When the cluster's usage is lower than the baseline, the cluster accumulates the unused RUs until the load on the cluster increases above the baseline. |
| burst performance | The ability of the Serverless cluster to perform above the baseline. Supporting application traffic that "bursts," i.e., can fluctuate above baseline traffic, is a key feature of Serverless clusters. Every Serverless cluster starts with a certain amount of burst performance capacity. If the actual usage of a cluster is lower than the baseline performance, the cluster can earn Request Units that can be used for burst performance for the rest of the month. |
| storage | Disk space for permanently storing data over time. All data in CockroachDB Serverless is automatically replicated three times and distributed across Availability Zones to survive outages. Storage is measured in units of GiB-months, which is the amount of data stored multiplied by how long it was stored. Storing 10 GiB for a month and storing 1 GiB for 10 months are both 10 GiB-months. The storage you see in the Cluster Overview page is the amount of data before considering the replication multiplier. |
CockroachDB Dedicated
If you need a single tenant cluster with no shared resources, we recommend CockroachDB Dedicated. CockroachDB Dedicated supports single and multi-region clusters in Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud Platform. CockroachDB Dedicated is recommended for all workloads: lightweight and critical production.
Hardware
We use the Kubernetes offerings in AWS and GCP (EKS and GKE respectively) to run CockroachDB Cloud offerings. GCP clusters use N1 standard machine types and Persistent Disk storage. AWS clusters use M5 instance types and Elastic Block Store (EBS). Each single-region cluster has a minimum of three nodes spread across three availability zones (AZ) in a cloud provider region. Multi-region clusters are similar to single-region clusters, with nodes spread across three or more AZs in each region.
Security and Connection
CockroachDB Dedicated clusters are single tenant. This means each new cluster gets its own project in GCP or its own account in AWS. No two CockroachDB Dedicated clusters share any resources with each other. Since these clusters are within their own accounts and projects, they are also in a default virtual private cloud (VPC). Users connect to a CockroachDB Dedicated cluster by using a load balancer in front of each region which leads to one connection string per region. Unless you set up VPC peering or AWS PrivateLink, your cluster will use TLS 1.3 protocol for encrypting inter-node and client-node communication.
CockroachDB Cloud clusters also use digital certificates for inter-node authentication, SSL modes for node identity verification, and password authentication for client identity verification. See Authentication for more details.
Backups are encrypted in S3 and GCS buckets using the cloud provider keys.
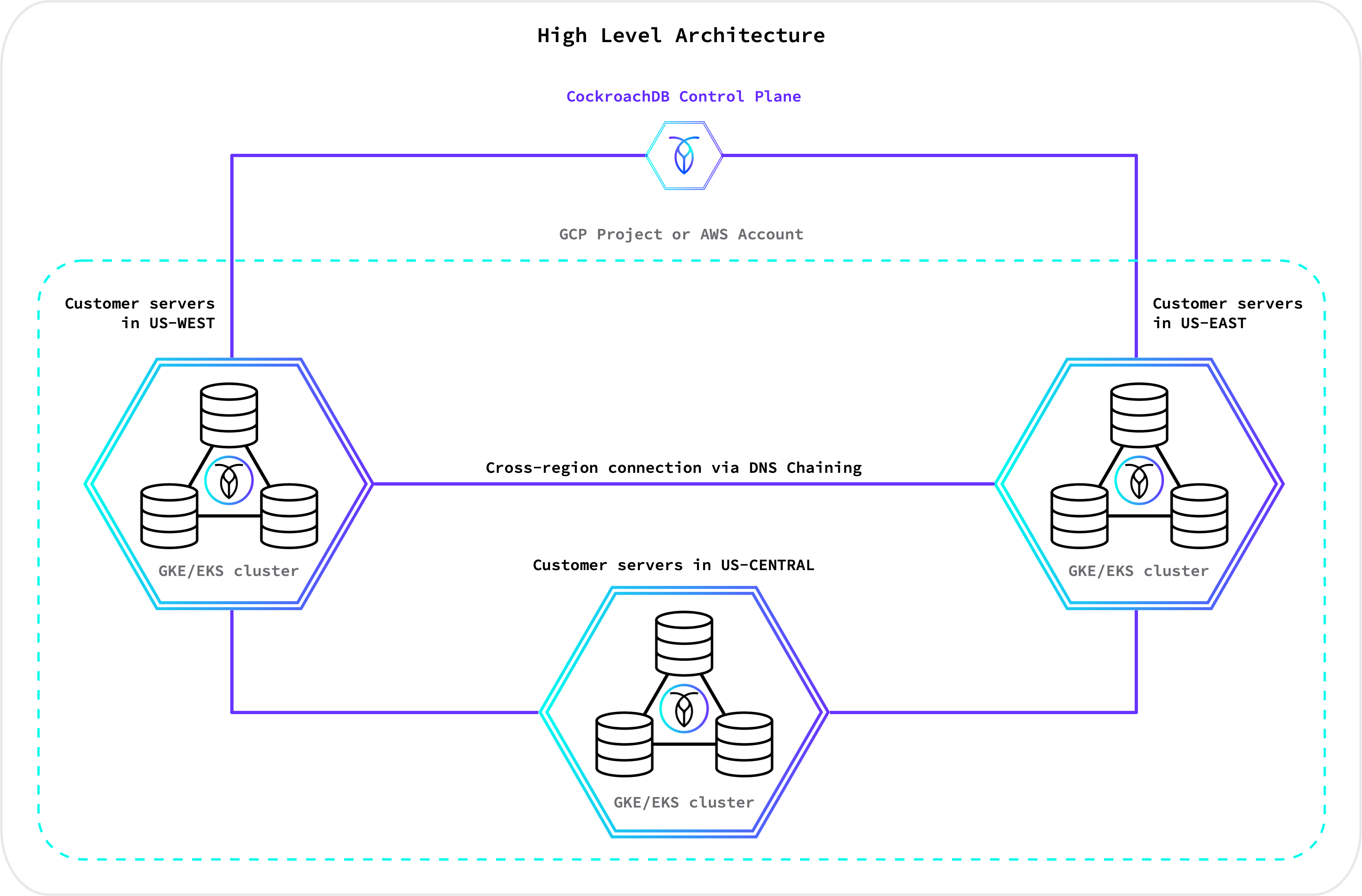
Multi-region architecture
The diagram below shows a high-level representation of a CockroachDB Dedicated multi-region cluster:
CockroachDB Serverless
CockroachDB Serverless is a fully-managed, auto-scaling deployment of CockroachDB. Being familiar with the following concepts will help you understand our Serverless architecture. CockroachDB Serverless is ideal for lightweight applications, starter projects, development environments, and proofs of concept.
Architecture
CockroachDB Serverless is a managed multi-tenant deployment of CockroachDB. A Serverless cluster is an isolated, virtualized tenant running on a much larger physical CockroachDB deployment.
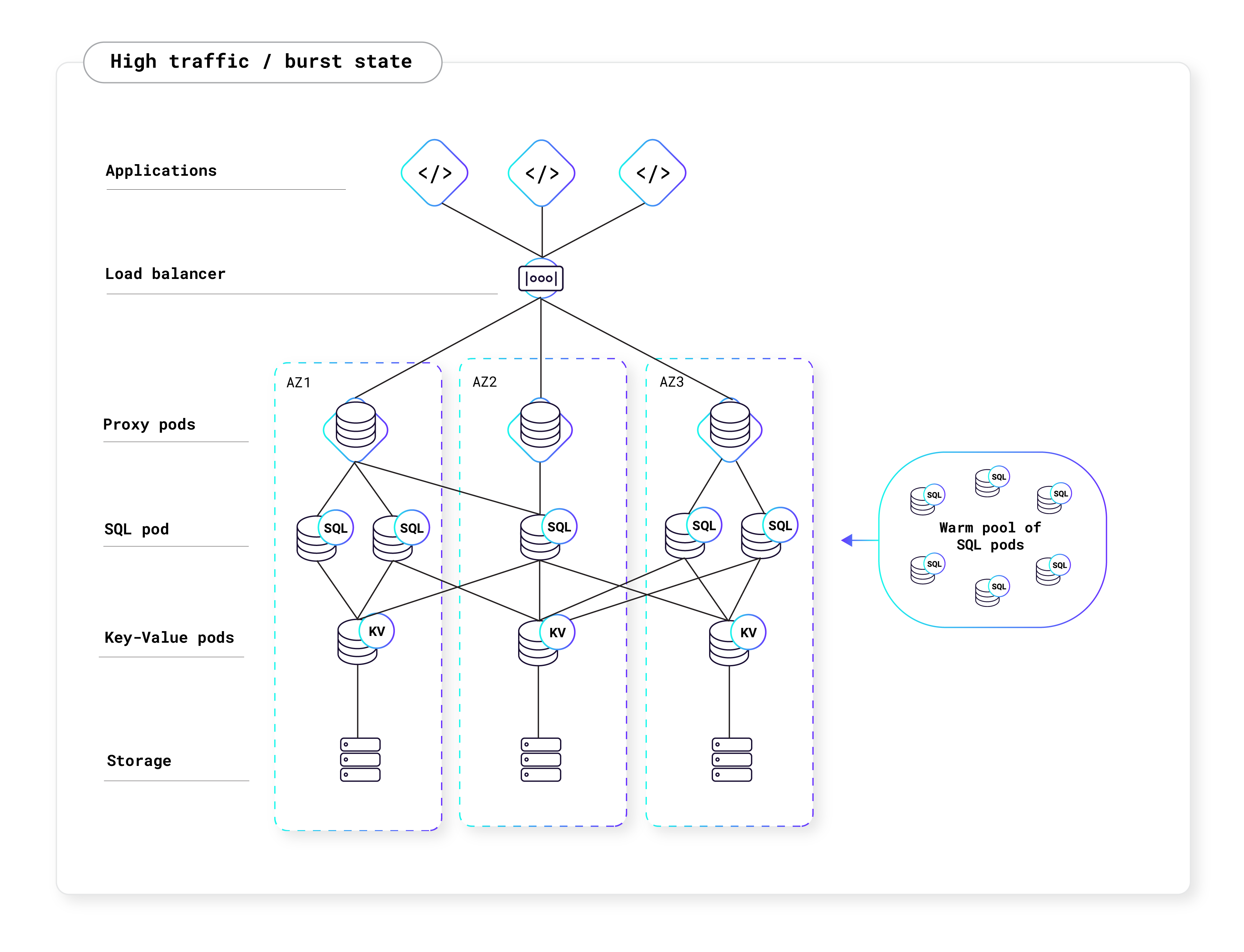
CockroachDB Serverless has separate compute and storage layers. The storage pods (KV pods) can be shared across users, and the compute pods (SQL pods) are unique to each user. These shared resources make CockroachDB Serverless architecture "multi-tenant," in contrast to the single tenant architecture of CockroachDB Dedicated.
Traffic comes in from the public internet and is routed by the cloud provider’s load balancer to a Kubernetes (K8s) cluster that hosts CockroachDB. K8s pods allow CockroachDB Serverless to limit SQL resource consumption for each user. They also minimize interference between pods that are scheduled on the same machine, giving each user a high-quality experience even when other users are running heavy workloads.
The following diagram is a high-level representation of what a typical Serverless cluster looks like:
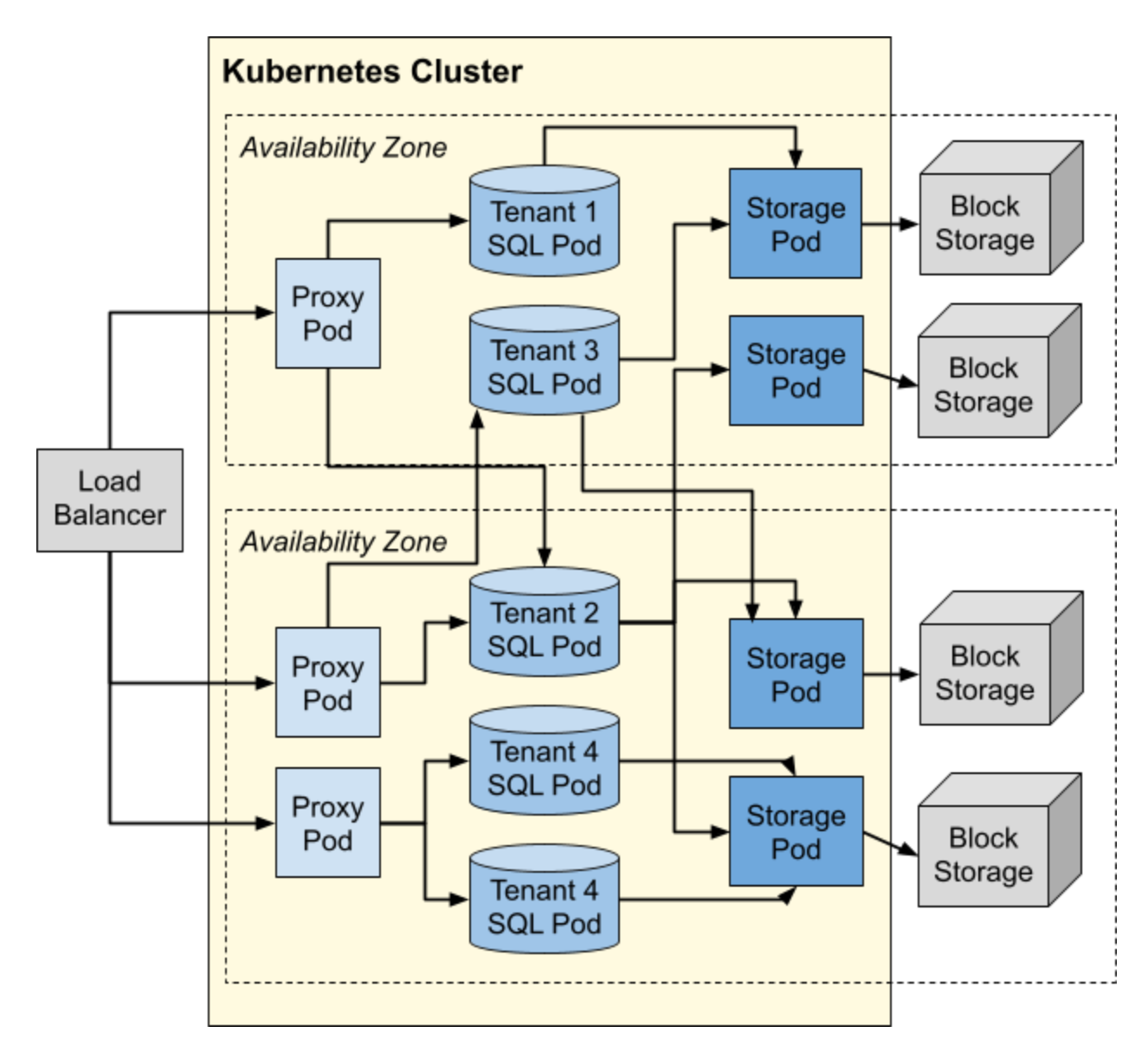
Proxy pods allow many users to share the same IP address, balance loads across a user's available SQL pods, and automatically resume clusters that have been paused due to inactivity. They also detect and respond to suspected abuse of the service.
After the cloud load balancer routes a new connection to one of the proxy pods, the proxy pod will in turn forward that connection to a SQL pod owned by the connecting user. Each SQL pod is dedicated to just one user, and multiple SQL pods can be owned by the same user. Network security rules prevent SQL pods from communicating with one another unless they are owned by the same user.
Finally, the SQL pods communicate with the KV layer to access data managed by the shared storage pods, each of which stores that data in an AWS or GCP block storage system.
Performance
Baseline
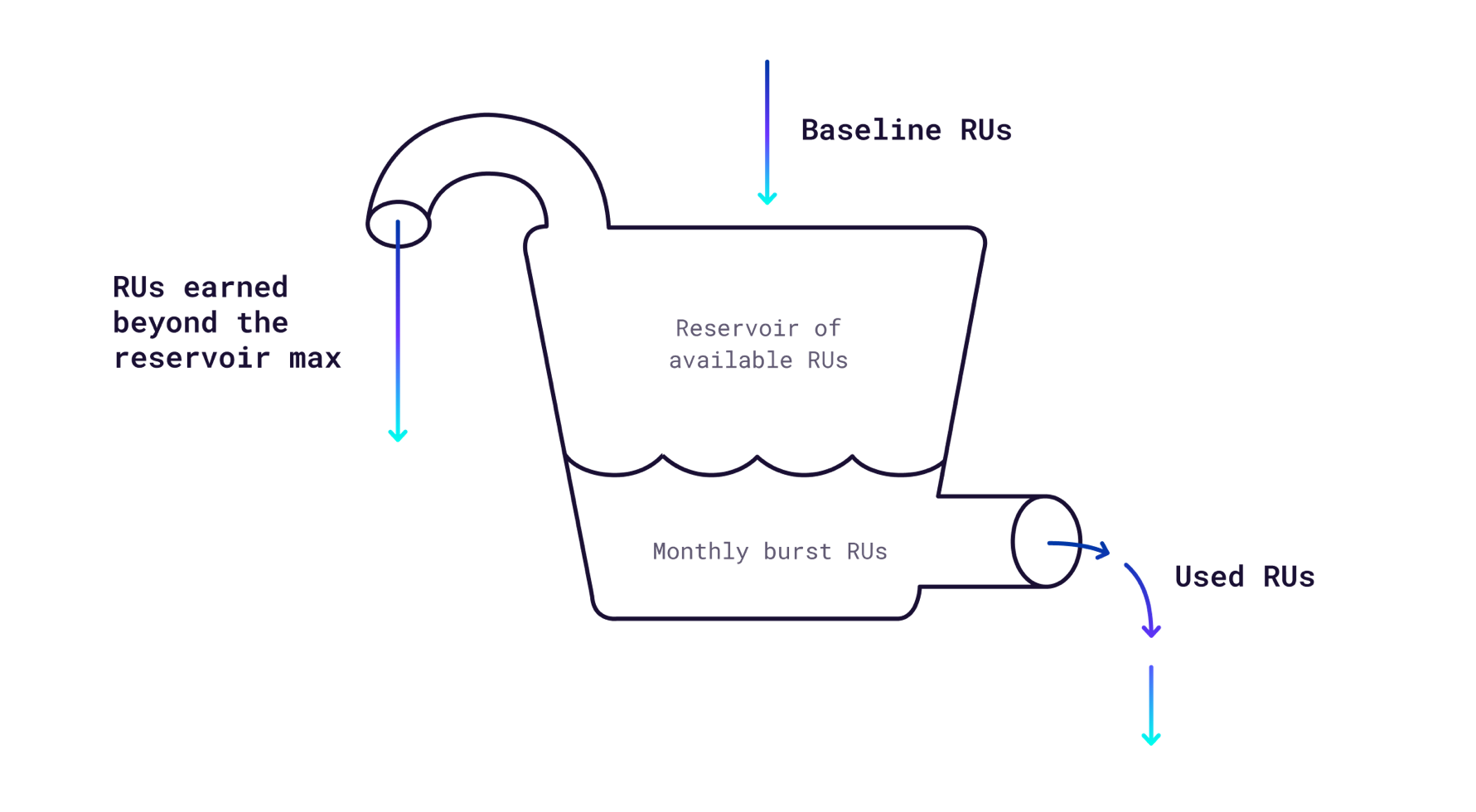
Baseline performance for a Serverless cluster is 100 RUs per second, and any usage above that is called burst performance. Clusters start with 10M RUs of free burst capacity each month and earn 100 RUs per second up to a maximum of 250M free RUs per month. Earned RUs can be used immediately or accumulated as burst capacity. If you use all of your burst capacity, your cluster will revert to baseline performance.
The following diagram shows how RUs are accumulated and consumed:
Paid
You can set your spend limit higher to maintain a high level of performance with larger workloads. If you have a spend limit, your cluster will not be throttled to baseline performance once you use all of your free earned RUs. Instead, it will continue to use burst performance as needed until you reach your spend limit. You will only be charged for the resources you use up to your spend limit. If you reach your spend limit, your cluster will revert to the baseline performance of 100 RUs per second.
Depending on your workload, your budget will be used differently. For example, a cluster using very little storage space will have more of its budget available for burst performance, and vice versa. If you hit your spend limit, your cluster will be throttled down to baseline performance levels. If this occurs, you can opt to increase your spend limit, adjust your workload to stay within the current spend limit, or stay at the baseline performance level until the next month.
Storage always gets first priority in the budget since you need to be able to store your data first and foremost. The remainder of the budget is allocated to burst performance. You can theoretically reach your spend limit on burst performance in the first few minutes of a cluster being created. If this happens, the cluster will be throttled back to the baseline performance and can reaccumulate burst capacity by using fewer RUs.
Autoscaling
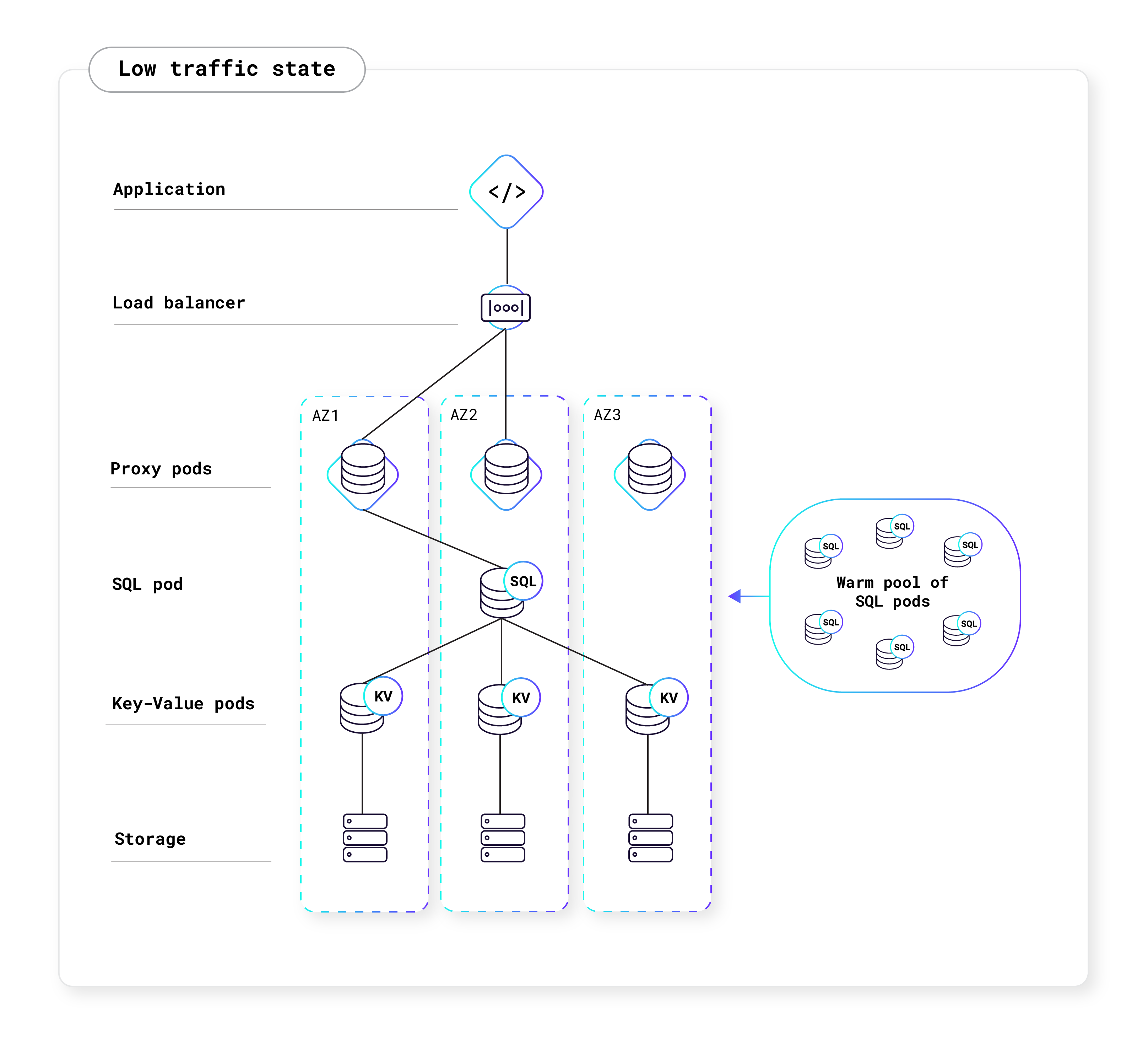
Serverless clusters also have the ability to scale to zero and consume no compute resources when there are no active queries. When there are no active queries, you will pay for the storage your app is using, but not for Request Units. To avoid wasted resources, CockroachDB Cloud automatically pauses Serverless clusters that are inactive, which is defined by having no connection to the cluster for five consecutive minutes. Once the user attempts to reconnect to the cluster, the cluster will automatically resume. Pausing, resuming, and scaling clusters is a fully-managed process and will not disrupt or affect the user experience. However, it is important for your application to have connection retry logic in the event of node restarts or network disruptions. For more information, see the Production Checklist.
The diagrams below shows how CockroachDB Serverless autoscales with your application's traffic:
Learn more
See the CockroachDB architecture documentation for more information.