This page describes how to plan your CockroachDB Dedicated or CockroachDB Serverless cluster.
Planning your cluster
Before making any changes to your cluster's configuration, review the requirements and recommendations for CockroachDB Cloud clusters.
Request Units
CockroachDB Serverless cluster resource usage is measured by two metrics: storage and Request Units, or RUs. RUs represent the compute and I/O resources used by a query. All database operations cost a certain amount of RUs depending on the resources used. For example, a "small read" might cost 2 RUs, and a "large read" such as a full table scan with indexes could cost a large number of RUs. You can see how many Request Units your cluster has used on the Cluster Overview page.
Cluster scaling
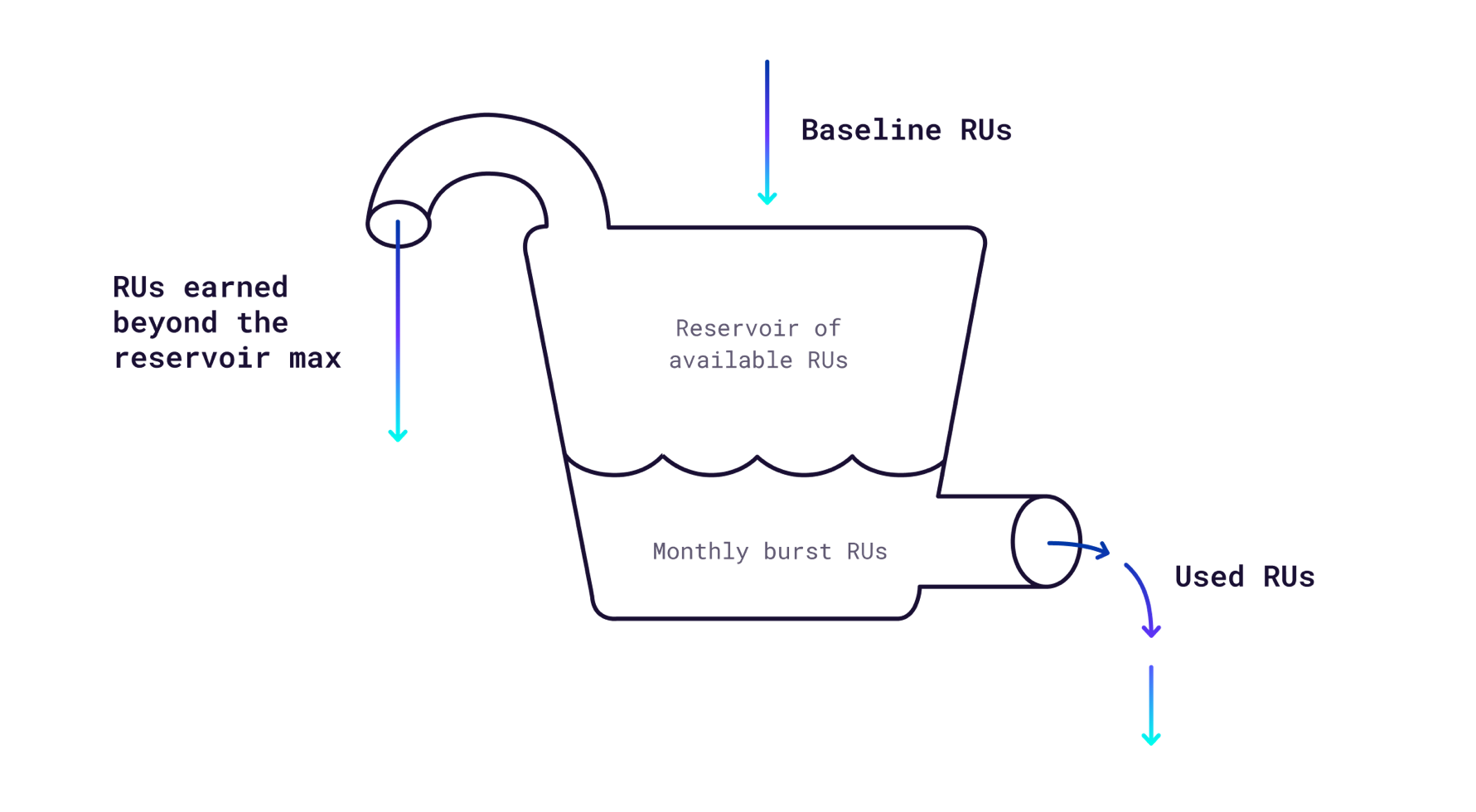
CockroachDB Serverless clusters scale based on your workload. Baseline performance for a Serverless cluster is 100 RUs per second, and any usage above that is called burst performance. Clusters start with 10M RUs of free burst capacity each month and earn 100 RUs per second up to a maximum of 250M free RUs per month. Earned RUs can be used immediately or accumulated as burst capacity. If you use all of your burst capacity, your cluster will revert to baseline performance.
You can set your spend limit higher to maintain a high level of performance with larger workloads. If you have set a spend limit, your cluster will not be throttled to baseline performance once you use all of your free earned RUs. Instead, it will continue to use burst performance as needed until you reach your spend limit. You will only be charged for the resources you use up to your spend limit. If you reach your spend limit, your cluster will revert to the baseline performance of 100 RUs per second.
The following diagram shows how RUs are accumulated and consumed:
Resource usage
The best way to estimate your resource usage is to enter a spend limit you're comfortable with and run your workload. You can see the RUs and storage your cluster has used in the Usage this month section of the Cluster Overview page. Once enough usage data is available, you can also see a graph of your monthly resource usage and recommended spend limit on the Edit cluster page. For a tutorial on estimating your CockroachDB Serverless usage using a sample workload, see Estimate Serverless Usage with MovR.
All Console Admins will receive email alerts when your cluster reaches 75% and 100% of its burst capacity or storage limit. If you set a spend limit, you will also receive alerts at 50%, 75%, and 100% of your spend limit.
Serverless Example
Let's say you have an application that processes sensor data at the end of the week. Most of the week it handles only occasional read requests and uses under the 100 RUs per second baseline. At the end of the week the sensors send in their data to the application, requiring a performance burst over the 100 RUs per second baseline. When the cluster requires more than 100 RUs per second to cover the burst, it first spends the earned RUs that accrued over the previous week and the 10M free burst RUs given to the cluster each month.
If you have a free cluster, it will be throttled to baseline performance once all of the free and earned burst RUs are used. The sensor data will still be processed while the cluster is throttled, but it may take longer to complete the job. If you have set a spend limit set, the cluster will be able to scale up and spend RUs to cover the burst, up to your maximum spend limit. If you reach your spend limit at any point during the month, your cluster will be throttled to baseline performance.
If your cluster gets throttled after using all of its burst capacity during the high load period, it will still earn RUs during lower load periods and be able to burst again. At the end of the month, your usage will reset and you will receive another 10M free burst RUs.
Cluster configuration
A single node cluster is only appropriate for single-region application development and testing. For single-region production deployments, we recommend a minimum of 3 nodes. The number of nodes you choose also affects your storage capacity and performance. See the Example for more information.
All CockroachDB Cloud clusters use 3 Availability Zones (AZs). For balanced data distribution and best performance, we recommend using a number of nodes that is a multiple of 3 (e.g., 3, 6, or 9 nodes per region).
Multi-region clusters
Multi-region clusters must contain at least 3 regions to ensure that data replicated across regions can survive the loss of one region. For example, this applies to internal system data that is important for overall cluster operations as well as tables with the GLOBAL table locality or the REGIONAL BY TABLE table locality and REGION survival goal.
Each region of a multi-region cluster must contain at least 3 nodes to ensure that data located entirely in a region can survive the loss of one node in that region. For example, this applies to tables with the REGIONAL BY ROW table locality. We recommend you use the same number of nodes in each region of your cluster for best performance and stability.
You can have a maximum of 9 regions per cluster through the Console. If you need to add more regions, contact us.
Cluster scaling
When scaling up your cluster, it is generally more effective to increase node size up to 16 vCPUs before adding more nodes. For example, if you have a 3 node cluster with 2 vCPUs per node, consider scaling up to 8 vCPUs before adding a fourth node. For most production applications, we recommend at least 4 to 8 vCPUs per node.
We recommend you add or remove regions or nodes from a cluster when the cluster isn't experiencing heavy traffic. Adding or removing nodes incurs a non-trivial amount of load on the cluster and takes about 30 minutes per region. Changing the cluster configuration during times of heavy traffic can result in degraded application performance or longer times for node modifications. Before removing nodes from a cluster, ensure that the reduced disk space will be sufficient for the existing and anticipated data. Before removing regions from a cluster, be aware that access to the database from that region will no longer be as fast.
If you have changed the replication factor for a cluster, you might not be able to remove nodes from the cluster. For example, suppose you have a 5-node cluster and you had previously changed the replication factor from its default value of 3 to 5. Now if you want to scale down the cluster to 3 nodes, the decommissioning nodes operation might fail. To successfully remove nodes from the cluster in this example, change the replication factor back to 3, and then remove the nodes.
Dedicated Example
Let's say you want to create a cluster to connect with an application with a requirement of 2000 TPS that is running on the Google Cloud Platform in the us-east1 region.
Suppose the raw data amount you expect to store without replication is 500 GiB. At 40% compression, you can expect a savings of 200 GiB, making the amount of data you need to store is 300 GiB.
Assume a storage buffer of 50% to account for overhead and data growth. The net raw data amount you need to store is now 450 GiB.
With the default replication factor of 3, the total amount of data stored is (3 * 450 GiB) = 1350 GiB.
To determine the number of nodes and the hardware configuration to store 1350 GiB of data, refer to the table in Create Your Cluster. One way to reach a 1350 GiB storage capacity is 3 nodes with 480 GiB per node, which gives you a capacity of (3*480 GiB) = 1440 GiB.
Let's see how many vCPUs you need to meet your performance requirement of 2000 TPS. We don't recommend 2 vCPU nodes for production, so the first compute configuration you should check is 3 nodes with 4 vCPUs per node. This configuration has (3*4 vCPUs) = 12 vCPUs. Since each vCPU can handle around 1000 TPS, a configuration of 4 vCPUs per node meets your performance requirements.
Your final configuration is as follows:
| Component | Selection |
|---|---|
| Cloud provider | GCP |
| Region | us-east1 |
| Number of nodes | 3 |
| Compute | 4 vCPU |
| Storage | 480 GiB |